Overview |
|
|
The Data File Parser is a graphical user interface for parsing data files that are processed according to a Data File Definition.
In this context, "parsing" refers to creating Fields associated with data (in a cell or range of cells) and mapping the data to the Fields. The Processing script (Groovy or Action Block) references these Fields and mapping information when processing the data file, ie., importing the data into LabVantage.
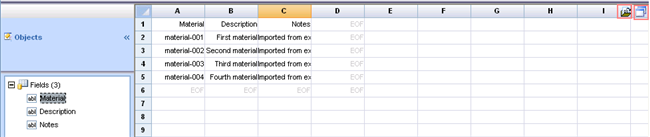
After loading an example file, click the File from the list to open the Data File Parser. The user interface is similar to the Form Builder, i.e., Objects in the upper left frame, Properties (for Fields) in the bottom left frame, and Grid (spreadsheet) in the right frame. The Grid shows data from the example file in rows-by-columns format. You can select cells, rows, columns, and ranges (similar to Excel).
| Frame | Description |
| Grid (right) |
Spreadsheet-like representation of data in the example file. |
| Properties Frame (lower left) |
Lets you view and set properties of the Field selected in the Objects frame. |
| Objects Frame (upper left) |
Shows fields defined on the Grid. Clicking a Field shows in properties in the Properties frame. |
Icons in the Data File Parser page |
| Icons | Description |
|
|
Loads an Example File. |
|
|
Maximizes/Minimizes the editor. |
styles |
|
|
| General Information |
These acronyms are displayed in the Grid to define a cell's position relative to the data:
| Acronym | Meaning | Description |
| EOF | End of File | Last column or row containing data. |
| FBC | First Blank Column | First blank column encountered. |
| FBR | First Blank Row | First blank row encountered. |
For example, selecting from cell "A1" to "A EOF" means that the selection is in column A, and from row 1 down to the physical end of rows.
| Simple Grid |
A "Simple Grid" is a basic grid as shown in the example below. Your Example File must match this format.
| A | B | C | D | E | |
| 1 | SampleId | SampleType | Description | AnalystId | CreatedDt |
| 2 | S-001 | Finished | For production. | GK | 2/2/2048 |
| 3 | S-002 | QC | For test. | LP | 2/2/2048 |
| 4 | S-003 | QC | For test. | US | 2/2/2048 |
| 5 | S-004 | Finished | For production. | TP | 2/2/2048 |
You can define "Column" Fields (a Range of rows in one column), "Row" Fields (a Range of columns in one row), or "Cell" Fields (individual cells).
| Crosstab Grid |
A "Crosstab" is a more sophisticated grid with headers as shown in the example below. A Crosstab can consist of:
| • | A"Range" Field |
| • | Zero or more "header Row" Fields |
| • | Zero or more "header Column" Fields |
| • | Zero or more "Cell" Fields |
Below is an example of a Crosstab layout with 3 header Rows, 2 header Columns, and a Range Field consisting of cells B4 through C9. In general, your Example File must match this kind of format (although in practice you can have a different number of headers, such as 1 header Column and 1 header Row).
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
During processing (when data are created for the Fields), a Crosstabbed grid is "de-crosstabbed". The example below shows how this is done. First, the Range Field is linearized (column B below right). Next, the header Column is replicated once for each column in the Range (column A). Then the header cells Au(1) and Zn(1) are replicated once for each item in the Target Range (column C).
|
→ |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
"Decrosstabbed" |
| Freeform |
This can have any type of Fields. It encompasses functionality of Crosstab grids, but allows other undetermined options to be exercised.
| Composite |
A "Composite" lets you import multiple Excel Worksheets (of dependent data) within the same Data File. Composite DFDs consist of an ordered sequence of child DFDs, each corresponding to a different Worksheet within the same Data File. Since Composite DFDs rely on Excel Worksheets to provide the child DFD import, only Excel file formats are supported (not text/csv files).
Choosing the "Composite" style removes the Parser and Processing details and adds the Data File Definition detail upon Saving.
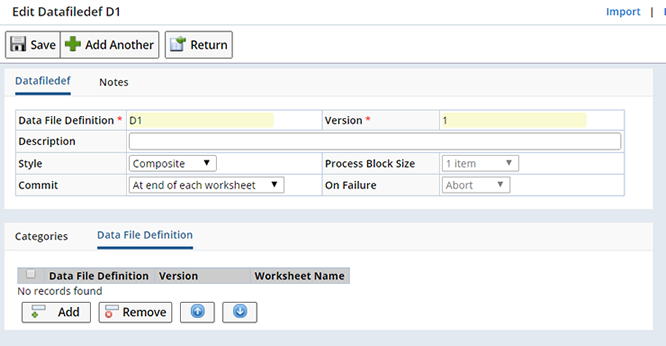
Define the Data File
The Data File must be a multi-worksheet Excel file that includes the required sheet names. You will then create a DFD file for each sheet.
For example, MasterDataImport requires two worksheets Param and ParamList.
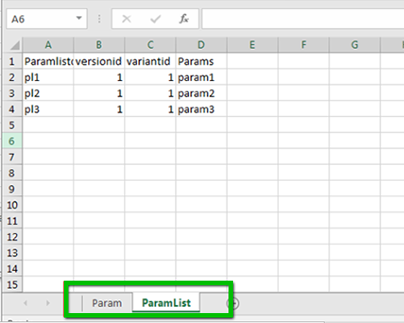
List the child DFDs (sheets)
For each sheet, include a child Data File. In the Data File Definition detail, include each child DFD (a child DFD must not be a "Composite" DFD).
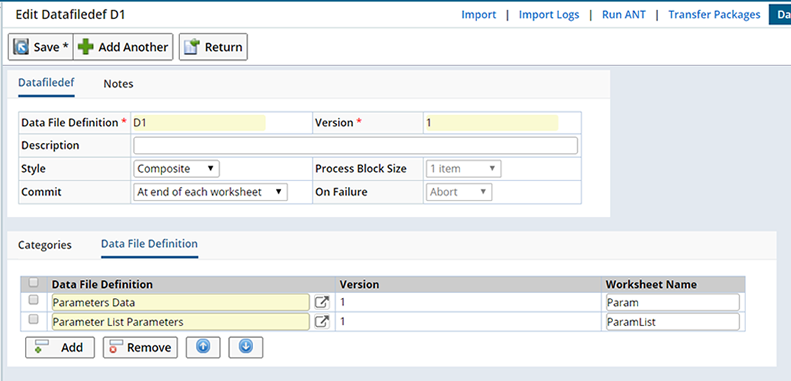
Be sure the DFDs are listed in the same order as the sheets of the Excel file, Child DFDs are imported in the exact order specified in the Data File Definition detail. You can change the sheet Name specified in the Child DFD.
| NOTE: | If you attempt to import a file that does not have the required worksheets, you will not be allowed to proceed. Click the Back button to upload another file. |
Define the Commit Scope
"Process Block Size" and "On Failure" action are defined within each child DFD and can not be defined for the Composite DFD. You can however define the Commit Scope for the Composite DFD.
| Option | Description |
| At end of each worksheet | This option requires each child DFD to ignore its processing options commit size. Each child DFD will commit its data at the end of the import of a single worksheet. Composite DFD import, calls the ImportDataFile for each child DFD with an overriding property called COMMITSCOPE = "ALL". This indicates that the transaction is to be committed at the end of "ALL" the records in the worksheet being processed. |
| Defer to child commit rules | This option is the default for all Composite processing. Each child DFD determines the Commit Scope based on the child DFD definition. The Composite does not drive the Commit scope. |
| When action is committed | This option commits the entire import operation when all the import actions are committed. Composite DFD import, calls the ImportDataFile for each child DFD with an overriding property called COMMITSCOPE = "NONE". This makes sure the child DFD import is not committed until all the child DFDs are committed. |
During Import, if the uploaded file has all the required worksheets, the wizard indicates that the check has passed.
Validation Log
A Validation log is displayed in a single table for all worksheets. An additional column indicates which worksheet contains errors or warnings (if any). If any of the worksheets have Errors, the import cannot proceed.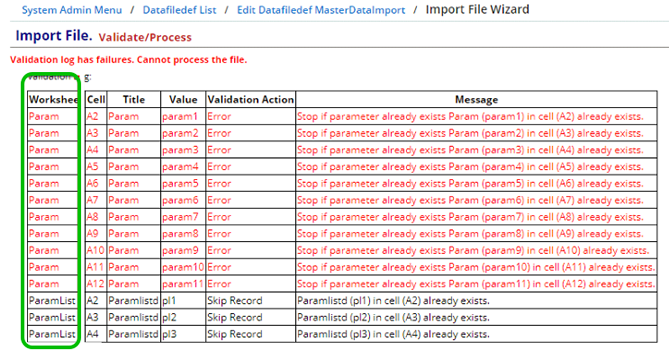
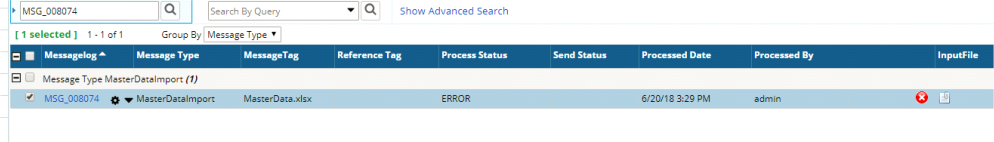
A single message log entry is created for a Composite DFD import. The Validation Log and Process Log display the Message Log for each child DFD import.
Fields |
|
|
Creating and Removing Fields |
To create a Field:
| 1. | Select data in accordance with the style, right click within the selection, then select "Add To New Field". | |
| 2. | In the resulting dialog, specify a Field Id (identifier for the Field), a title (user-friendly version of the Field Id), title and other necessary properties. The dialog automatically detects the type of selection (such as column, row, headercolumn). | |
| 3. | Click OK. The Field is created and appears in the Objects frame. |
You can right-click a Field object in the Objects frame to create a field either from a selection ("Add Field from Range"), or from scratch ("Add Empty Fields").
To highlight all Fields in the grid, right-click the Field, then select "Highlight Fields".In addition you can also create fields of type "input" by choosing the option "Add Input Field". See Field Types for details.
To remove an existing Field, right-click the Field, then select "Remove Field".
When you click a Field in the Objects frame, the range is selected in the grid and the Field properties are loaded into the Properties frame. You can then edit the properties for that Field.
Field Types |
The Types of Fields you can create depend on the style you select in the Data File Definition Maintenance page:
| style | Allowable Field Types |
| Simple Grid | Cell |
| Row | |
| Column | |
| Input | |
| Crosstab Grid | Cell |
| Range | |
| header Row | |
| header Column | |
| Input | |
| Freeform | All |
Note the "Input" Field Types. "Input" fields correspond to additional properties that will be passed on to the ImportDataFile Action. Input fields are available in the Processing Rules definition (as is the case with the other fields). The name of the input field should correspond to the name of the input property passed to ImportDataFile. At run time, the value of the input fields is determined from the input properties to the ImportDataFile Action.
Data Types |
Several of the Field Properties below let you declare a Data Type. The Data File Parser drives the parsing of data from Excel files as follows:
| Excel Cell Format | LabVantage Data Type | Data File Parser Conversion |
| String | String | The Excel string is parsed without modification. |
| String | Number | The Excel string must correspond to a valid numeric string in the User's locale. Parsing errors are reported at runtime. |
| String | Date | The Excel string must correspond to a valid date string in the User's locale. Parsing errors are reported at runtime. |
| Number | String | The Excel numeric value is converted to a string. Formatting specified in Excel is retained. |
| Number | Number | The Excel numeric value is converted to a numeric string in the User's locale, then passed to the Actions in the processing script. |
| Number | Date | The Data File Parser throws an error. |
| Number DateFormatted |
String | The Excel date value is converted to a string. Formatting specified in Excel is retained. |
| Number DateFormatted |
Number | The Data File Parser throws an error. |
| Number DateFormatted |
Date | The Excel date value is converted to a date string in the User's locale, then passed to the Actions in the processing script. |
Field Properties |
Here are the Field Properties supported by each Field Type and style.
| Cell (Simple Grid and Crosstab Grid) |
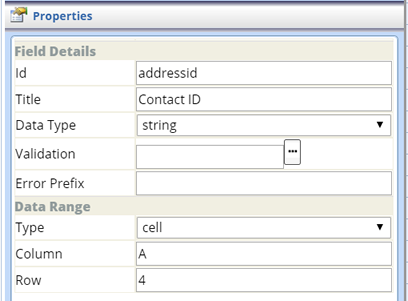
Field Details
| Property | Description |
| Id | Identifier of the Field. |
| title | User-friendly alias to display in place of the Id (above). |
| Data Type | LabVantage Data Type that defines the selected data (string, number, or date). |
| Validation | Define Validation Rules for this field. |
| Error Prefix | In the Validation Log, this prefix is appended to any
generated Validation errors. For example, if validation requires the Subject
Id to be unique, the Error Prefix for the subjectid field might be "This
Subject must be unique.". This prefix becomes part of the validation
log to help identify the validation error. |
Data Range
| Property | Description |
| Type | Field Type (defaults to "cell"). |
| Column | Coordinates of the cell defined for the Field (number of the column and row). |
| Row |
| Row (Simple Grid) |
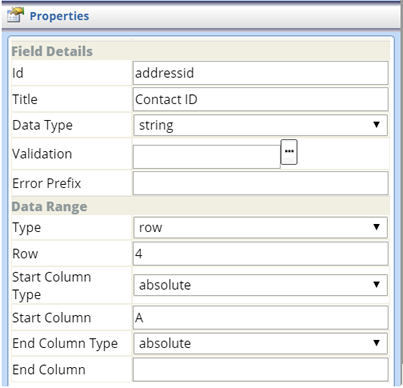
Field Details
| Property | Description |
| Id | Identifier of the Field. |
| title | User-friendly alias to display in place of the Id (above). |
| Data Type | LabVantage Data Type that defines the selected data (string, number, or date). |
| Validation | Define Validation Rules for this field. |
| Error Prefix | In the Validation Log, this prefix is appended to any generated Validation errors. For example, if validation requires the Subject Id to be unique, the Error Prefix for the subjectid field might be "This Subject must be unique.". This prefix becomes part of the validation log to help identify the validation error. |
Data Range
| Property | Description | ||||||||
| Type | Field Type (defaults to "row"). | ||||||||
| Row | Number of the row defined for the Field. | ||||||||
| Start Column Type | Defines how the first column in the Range is determined:
|
||||||||
| Start Column | First column in the Range. | ||||||||
| End Column Type | Defines how the last column in the Range is determined:
|
||||||||
| End Column | Last column in the Range. Applies only if "End Column Type" (above) is "absolute". |
| Column (Simple Grid) |
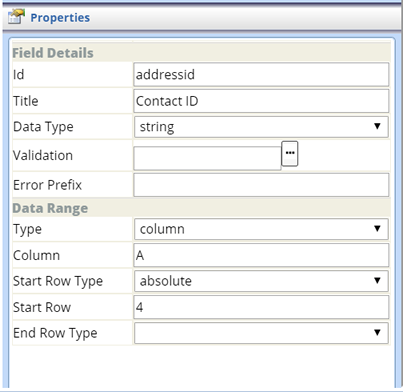
Field Details
| Property | Description |
| Id | Identifier of the Field. |
| title | User-friendly alias to display in place of the Id (above). |
| Data Type | LabVantage Data Type that defines the selected data (string, number, or date). |
| Validation | Define Validation Rules for this field. |
| Error Prefix | In the Validation Log, this prefix is appended to any generated Validation errors. For example, if validation requires the Subject Id to be unique, the Error Prefix for the subjectid field might be "This Subject must be unique.". This prefix becomes part of the validation log to help identify the validation error. |
Data Range
| Property | Description | ||||||||
| Type | Field Type (defaults to "column"). | ||||||||
| Column | Number of the column defined for the Field. | ||||||||
| Start Row Type |
Defines how the first row in the Range is determined:
|
||||||||
| Start Row | First row in the Range. | ||||||||
| End Row Type |
Defines how the last row in the Range is determined:
|
||||||||
| End Row | Last row in the Range. Applies only if "End Row Type" (above) is "absolute". |
| Range (Crosstab Grid) |
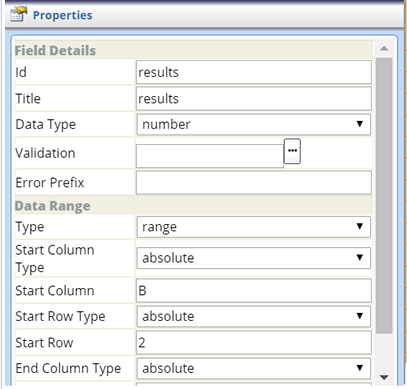
Field Details
| Property | Description |
| Id | Identifier of the Field. |
| title | User-friendly alias to display in place of the Id (above). |
| Data Type | LabVantage Data Type that defines the selected data (string, number, or date). |
| Validation | Define Validation Rules for this field. |
| Error Prefix | In the Validation Log, this prefix is appended to any generated Validation errors. For example, if validation requires the Subject Id to be unique, the Error Prefix for the subjectid field might be "This Subject must be unique.". This prefix becomes part of the validation log to help identify the validation error. |
Data Range
| Property | Description | ||||||||
| Type | Field Type (should default to "range", but currently says "cellrange"). | ||||||||
| Start Column Type | Defines how the first column in the Range is determined:
|
||||||||
| Start Column | First column in the Range. | ||||||||
| Start Row Type | Defines how the first row in the Range is determined:
|
||||||||
| Start Row | First row in the Range. | ||||||||
| End Column Type | Defines how the last column in the Range is determined:
|
||||||||
| End Column | Last column in the Range. Applies only if "End Column Type" (above) is "absolute". | ||||||||
| End Row Type | Defines how the last row in the Range is determined:
|
||||||||
| End Row | Last row in the Range. Applies only if "End Row Type" (above) is "absolute". |
| header Row (Crosstab Grid) |
A header Row Field defines a single row.
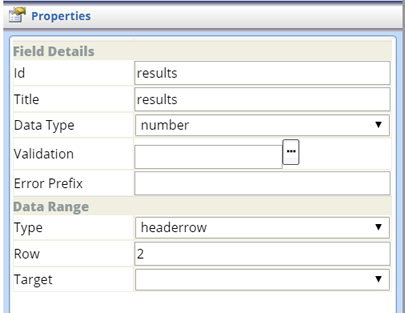
Field Details
| Property | Description |
| Id | Identifier of the Field. |
| title | User-friendly alias to display in place of the Id (above). |
| Data Type | LabVantage Data Type that defines the selected data (string, number, or date). |
| Validation | Define Validation Rules for this field. |
| Error Prefix | In the Validation Log, this prefix is appended to any generated Validation errors. For example, if validation requires the Subject Id to be unique, the Error Prefix for the subjectid field might be "This Subject must be unique.". This prefix becomes part of the validation log to help identify the validation error. |
Data Range
| Property | Description |
| Type | Field Type (defaults to "headerrow"). |
| Row | Number of the row defined for the Field. |
| Target | Range Field to which the header Row applies. |
Example
| header Column (Crosstab Grid) |
A header Column Field defines a single column.
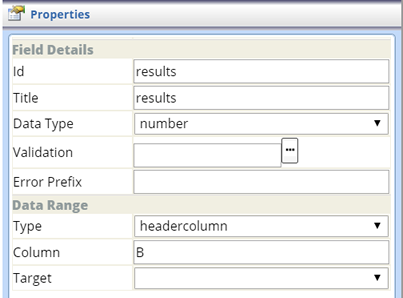
Field Details
| Property | Description |
| Id | Identifier of the Field. |
| title | User-friendly alias to display in place of the Id (above). |
| Data Type | LabVantage Data Type that defines the selected data (string, number, or date). |
| Validation | Define Validation Rules for this field. |
| Error Prefix | In the Validation Log, this prefix is appended to any generated Validation errors. For example, if validation requires the Subject Id to be unique, the Error Prefix for the subjectid field might be "This Subject must be unique.". This prefix becomes part of the validation log to help identify the validation error. |
Data Range
| Property | Description |
| Type | Field Type (defaults to "headercolumn"). |
| Column | Number of the column defined for the Field. |
| Target | Range Field to which the header Column applies. |
| Input Field (SimpleGrid) |
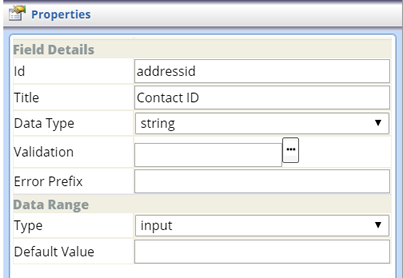
Field Details
| Property | Description |
| Id | Identifier of the Field. |
| title | User-friendly alias to display in place of the Id (above). |
| Data Type | LabVantage Data Type that defines the selected data (string, number, or date). |
| Validation | Define Validation Rules for this field. |
| Error Prefix | In the Validation Log, this prefix is appended to any generated Validation errors. For example, if validation requires the Subject Id to be unique, the Error Prefix for the subjectid field might be "This Subject must be unique.". This prefix becomes part of the validation log to help identify the validation error. |
Data Range
| Property | Description |
| Type | Field Type (defaults to "input"). |
| Default Value | Default Value of the input field, if any. |
| Input Field (CrosstabGrid) |
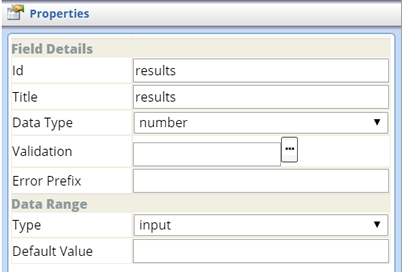
Field Details
| Property | Description |
| Id | Identifier of the Field. |
| title | User-friendly alias to display in place of the Id (above). |
| Data Type | LabVantage Data Type that defines the selected data (string, number, or date). |
| Validation | Define Validation Rules for this field. |
| Error Prefix | In the Validation Log, this prefix is appended to any generated Validation errors. For example, if validation requires the Subject Id to be unique, the Error Prefix for the subjectid field might be "This Subject must be unique.". This prefix becomes part of the validation log to help identify the validation error. |
Data Range
| Property | Description |
| Type | Field Type (defaults to "input"). |
| Default Value | Default Value of the input field, if any. |
| Input Field (Freeform) |
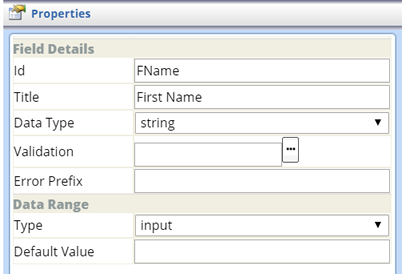
Field Details
| Property | Description |
| Id | Identifier of the Field. |
| title | User-friendly alias to display in place of the Id (above). |
| Data Type | LabVantage Data Type that defines the selected data (string, number, or date). |
| Validation | Define Validation Rules for this field. |
| Error Prefix | In the Validation Log, this prefix is appended to any generated Validation errors. For example, if validation requires the Subject Id to be unique, the Error Prefix for the subjectid field might be "This Subject must be unique.". This prefix becomes part of the validation log to help identify the validation error. |
Data Range
| Property | Description |
| Type | Field Type (defaults to "input"). |
| Default Value | Default Value of the input field, if any. |
Validation Rules |
|
|
Define Validation Rules when adding new or editing existing field properties. Click the ellipsis in the "Validation" field of the Field Properties to open the Validation Editor.
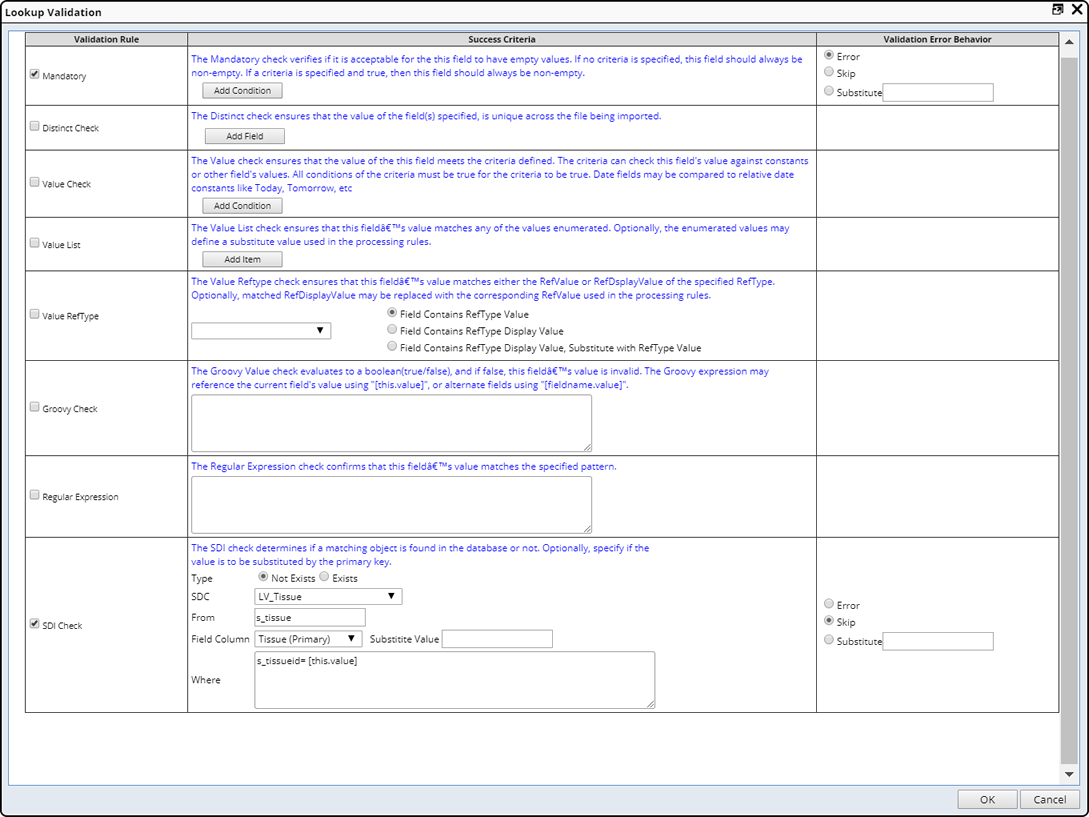
For each Validation Rule, specify Validation Error Behavior as one of the following (checking the Rule shows the Error Behavior options):
| Option | Description | |||
| Error | The import cannot proceed until the file is fixed. The error displays in "Red" in the Validation Log. | |||
| Skip | The "record" should not be processed if the success criteria is not met, the rest of the file is processed. A Warning is added to the Validation Log.
|
|||
| Substitute | Specify a replacement value for "rogue" values that did not meet the "Success Criteria" so that the import can proceed safely. A Warning is added to the Validation Log. |
Following is a list of each Validation Rule and associated options:
| Rule | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
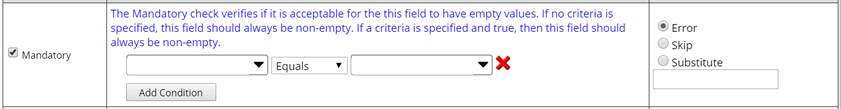
| Mandatory | Indicates whether or not a field value is mandatory. Choose to always require a value for this field, or click "Add Condition" to conditionally require a value.
When a Condition is defined (and exists), a value is required. For example, you might require that "Cigarettes per day" is required if the Subject is a Smoker. Each condition includes three parts:
Choose to include literal values in conditions for comparison. The following rules apply when specifying literals:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distinct Check | The Distinct Check rule lets you flag duplicate values
for a field, or a combination of fields, in the file being imported.
This rule applies for all Data Types. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
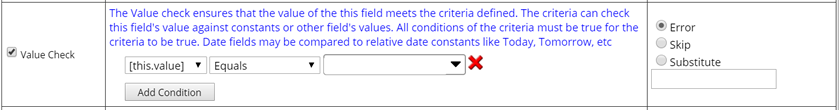
| Value Check | The Value Check rule allows you to compare the current field value against fixed values or values of other fields.
For example:
Each condition includes three parts:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
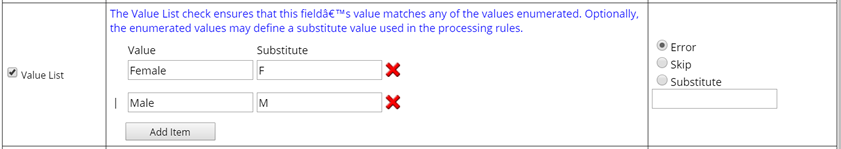
| Value List | This rule lets you check the current field value against a pre-defined list of values, then optionally substitute a string for each.
For example, you might create a list such as { "Male", "Female" } for the Gender field. The validation logic checks whether the field Value matches one of the Values in the list. Specify "Substitute" strings for each of the Values. When the field Values are passed to the Actions in the processing script, they are substituted as "M" or "F" instead of passing Male or Female (as is). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Value RefType | This rule lets you associate a Reference Type (ReftypeId) with the field.
Select the Reference Type with which the field value corresponds. Note that RefType includes the list "RefValues" and corresponding "RefDisplayValue".
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
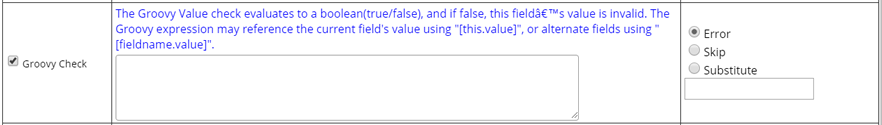
| Groovy Check | Lets you perform additional groovy checks that evaluate
to "Y" or "N" (True/False).
For example: For the field "Age" of type "number", you can have the following Check:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Regular Expression | Validates the field value against a regular expression.
Valid Email ID:
If the value of the field matches the pattern, the validation is successful. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
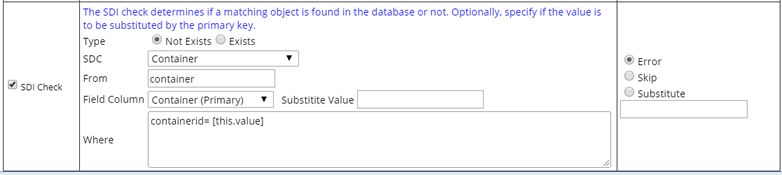
| SDI Check | This validation rule lets you check whether the SDI corresponding
to the current field value exists (or not) in the database.
For example, you might want to check that:
Substitute Keycolid This option can be used in conjunction with the "Exists" check, where you not only want to check for an SDI by alternate keycolid, you want the value to be replaced by keycolid when processing.
If no rows are returned, there is a validation failure. Otherwise, the returned keycolid is substituted for the column value when processing. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number Format | When the Data Type is number, the Number Format validation is available.
Number Format lets you specify:
In the case of numeric columns, the generated data file may contain numbers generated using a particular Decimal Separator, and Group Separator.
The validation editor allows you to configure the Decimal Separator and Group Separator. If the parsing fails, the Error Actions are considered. You can choose to throw an "Error", "Skip" the record, or "Substitute" with a default value. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
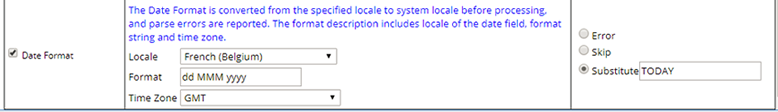
| Date Format | When the Data Type is "date", the Date Format
validation is available.
Date fields in the Data File may have a date format that is different from the date format of the User Importing the file. Date Format validation lets you parse the date correctly from any format by specifying a "Locale" and "Format" string. Additionally, a Time zone can be specified for the date field so that the time is adjusted before processing.
If the date field string cannot be parsed into an actual date, a default replacement can be specified as one of the Date Literals. |