Overview |
|
|
Data File Definitions let you import data from an Excel or text file into LabVantage. These formats are supported:
| File Extension | Description |
| xls / xlsx | Microsoft Excel. |
| csv | Text file with comma delimiters. |
| txt | Text file with configurable delimiters (comma, semicolon, and tab are preconfigured OOB). |
Essentially, importing data consists of:
| 1. | Creating a Data File Definition A "Data File Definition" is essentially a reusuable template that defines how data are mapped from a file to LabVantage and how the data are processed during the import. |
|
| 2. | Loading an Example File The "Example File" is the Excel or text file containing the data you want to import. Loading an example File puts it into the Data File Parser. |
|
| 3. | Define Fields using the Data File Parser In the "Data File Parser", you use Fields to map cells in the Example file to LabVantage. This allows the data to be imported into LabVantage. |
|
| 4. | Create a Processing Script Use Action Blocks or Groovy script to define the "Processing Script", which determines how LabVantage imports the data. For example, you can import Sample data, then have the Processing script Add the Samples as Sample SDIs. |
|
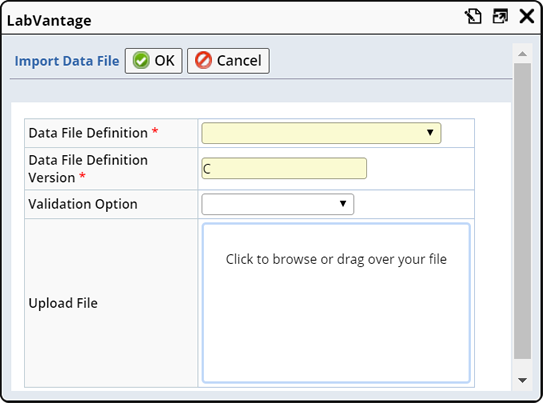
| 5. | Import the Data into LabVantage Data can be imported using the Configuration Transfer Tools, the ImportDataFile Action, or from LabVantage pages that are configured to use this functionality. |
Creating a Data File Definition |
|
|
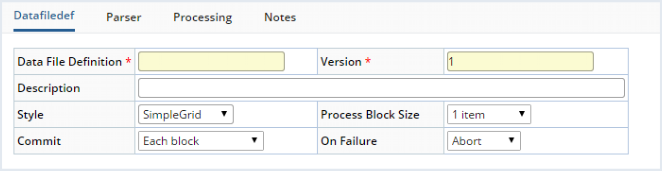
Create a Data File Definition through System Admin → System Tools → Data File Definitions.
|
| Setting | Description | ||||
| Data File Information | |||||
| Data File Definition | Identifier of the Data File Definition. | ||||
| Version | Version number of the Data File Definition. | ||||
| Description | Text description of the Data File Definition. | ||||
| style | Determines how data are presented during the Import. For descriptions, see styles in Data File Parser. | ||||
| Processing Options | |||||
| Process Block Size | Applies only to Simple Grid and Crosstab Grid styles:
|
||||
| Commit | Frequency at which the Blocks of data (defined by "Process
Block Size" above) are committed. For example, if "Process Block
Size" = 5 Items, a commit occurs "Every 5 blocks".
Choose "When action is committed" to ensure that the Import operation is not committed by the ImportDataFile Action. It is only committed when the action call itself is committed. |
||||
| On Failure | The entire transaction fails if any block fails. This
determines behavior in the event of a transaction failure:
|
||||
Loading an Example File |
|
|
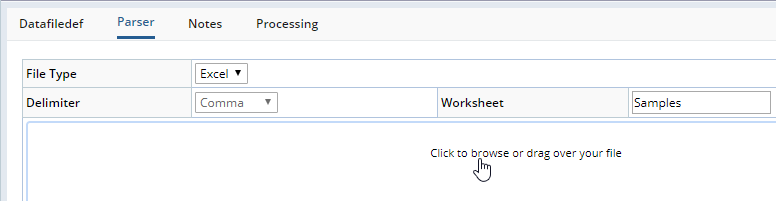
From the "Parser" tab, enter a Worksheet ID. Next, choose the file containing data you want to import and load it.
|
| Fields | Description |
| File Type | Determines the type of input file (Excel or Text). |
| Delimiter | If the File Type (above) is "Text", specifies the delimiter (comma, semicolon, or tab). |
| Worksheet | If the File Type (above) is "Excel", specifies the name of the Worksheet. You can import only one worksheet at a time. |
Following are the steps to load an Example File:
| 1. | Click the "Parser" tab. |
| 2. | Select the "File Type" as "Excel" or "Text". |
| 3. | If you have chosen "Excel", enter your Worksheet ID. |
| 4. | If the "File Type" is "Text", select a "Delimiter". |
| 5. | Browse and select the "Example File". |
| 6. | If the "File Type" is "Excel", enter
the Worksheet name, then click "OK". The Worksheet name is automatically
populated in the "Worksheet" field.
|
| 7. | Click the Example File. The selected file will be uploaded to the location specified in your File Location Policy under "Sapphire Custom. The Data File Parser opens. |
Defining Fields using the Data File Parser |
|
|
The Data File Parser lets you use Fields to map cells in the Example file to LabVantage. This is described in Data File Parser.
Creating a Processing Script |
|
|
The "Processing" tab lets you access the Action Block Script Editor. This is where you create the Processing Script (Groovy or Action Block ), which determines how LabVantage imports the data. Shown below is the OOB example "ExArrayZoneData" Form Fields mapped to the Actions.
As shown in Action Block Editor → Specifying Property Values as Groovy Expressions, you can also define and evaluate property values using Groovy expressions by pressing Alt-G. When using the Action Block Editor in a Data File Definition, special syntax is required if the Data File Definition's "Process Block Size" is set to more than 1 item. See Groovy Utilities for an example.
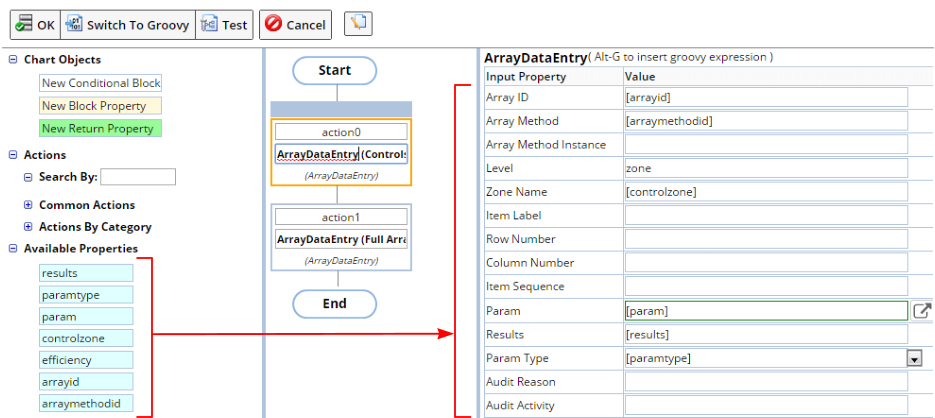
|
Importing the Data |
|
|
You have several import options:
| • | Configuration Transfer Tools
You can use the CTT Import wizard to import the data file. Choose "Data File" as the File Type. The data file must be on the machine hosting the Application Server. |
||||
| • | ImportDataFile
Action
"Input" fields can be passed into the ImportDataFile Action (see Field Types). |
||||
| • | List Pages
An "Import Data File" button is preconfigured OOB on List pages that allow upload of data files.
|
||||
| • | Data File Import | ||||
| • | Master Data Collection Tool |
This is a high-level view of what the Data File Definition provides during import:
About Message Types and Message Logs |
|
|
Each time you create a Data File Definition, a Message Type is created (the import request is actually a message).
A Message Log entry is thereby generated in the Message Log for every import operation. This feature can be disabled by the Message Type settings.
Groovy Utilities |
|
|
A set of Groovy utilities is provided to manipulate delimited strings, e.g., expand a single cell into a repeating semicolon-delimited string passed to an Action, or manage delimited strings needed in crosstab structures when calling LabVantage actions.
The propertyutil object (instance of the PropertyUtil class) can be accessed from Groovy in the processing rules. This object provides these methods:
| Method | Description | |||
| repeat | Repeats a basestring a specified number of times, delimited by the separator. | |||
| replaceListItems | The inputs can be an input string, a list of patterns,
and list of substitutes where there is a one-to-one correspondence between
the the items in patterns list and substitutes list. The return value
is a string, which is a transformation of input where every pattern is
substituted by its corresponding "substitute". Example:
input = id1, id1, id2, id2, id3, id3
|
|||
| addListItem | Adds a listitem to a basestring, separated by a specified delimiter. | |||
| isListItem | Checks if a basestring contains a specified listitem. | |||
| getListItemCount | Determines the number of items in a specified list. | |||
| getListItem | Retuns an item at a speicifed position in a list. | |||
| getUniqueItems | Takes a list of items with a separator (defaults to ; in first method) and eliminates duplicates.
String getUniqueItems( String list ) String getUniqueItems( String list, String separator )
For example: "S1;S1;S2;S3;S4;S4;S4" would be converted to "S1;S2;S3;S4" |